Application of medium temperature SCR in the cement industry
With the improvement of environmental protection standards, the emission standard of nitrogen oxides of cement plants in many provinces of China has been limited to 100 or 50 mg/m3, and the emission standard of ammonia has also reached 8 mg/m3 (even 5 mg/m3). In the past two years, Chinese cement enterprises began to install SCR systems, including high temperature SCR and medium temperature SCR. The author analyzes the denitration effect of medium temperature SCR and its influence on ammonia emission concentration in a 5000 t/d clinker line. Chinese cement plants are facing increasingly stringent environmental standards. Ultra-low emission standard of air pollutants for the cement industry [1] demands that NOx emission concentration is lower than 100 mg/m3 and ammonia slip is lower than 8 mg/m3. Many provinces have even stricter requirements which are NOx ≤ 50 mg/m3 and NH3 ≤ 5 mg/m3. In order to meet the emission standards, Chinese cement enterprises are trying many new denitration technologies, such as high temperature SCR, medium temperature SCR, LCR, etc. Only in 2021, Chinese cement enterprises have built 41 SCR denitration systems. The author analyzed the prospect of medium temperature SCR technology in the cement industry by introducing a 5000 t/d clinker line with medium temperature SCR.
1 Medium temperature SCR in the cement industry
1.1 SCR catalyst
SCR catalysts in the cement industry are generally divided into three types according to different temperatures: high temperature SCR catalyst, medium temperature SCR catalyst and low temperature SCR catalyst. The scope of high, medium and low temperature is not the same as that in the power industry, which is due to the characteristics of the cement industry itself. The working temperature range of high-temperature SCR catalyst in the cement industry is 280-350 °C, which is arranged between the outlet of cyclone one and the waste...
1 Medium temperature SCR in the cement industry
1.1 SCR catalyst
SCR catalysts in the cement industry are generally divided into three types according to different temperatures: high temperature SCR catalyst, medium temperature SCR catalyst and low temperature SCR catalyst. The scope of high, medium and low temperature is not the same as that in the power industry, which is due to the characteristics of the cement industry itself. The working temperature range of high-temperature SCR catalyst in the cement industry is 280-350 °C, which is arranged between the outlet of cyclone one and the waste heat boiler (WHB). The working temperature range of the medium temperature SCR catalyst is 200-250 °C, which is arranged between the waste heat boiler and the high temperature fan. The working temperature range of the low-temperature SCR catalyst is 100-150 °C, which is arranged between the filter and the exhaust fan [3, 4]. The high temperature SCR catalyst is a vanadium-titanium catalyst with vanadium content of 0.8~1.5%. The medium temperature SCR catalyst is also a vanadium-titanium catalyst with vanadium content of 2%~4%. We used a manganese-based low temperature SCR catalyst for the industrial test in a cement enterprise. The experimental results show that the manganese-based catalyst can achieve a denitration efficiency of more than 80% in industrial application. However, considering that the manganese-based catalysts are prone to sulfur poisoning, the denitration efficiency and catalyst life are affected by the sulfur dioxide content. At present, the main research of low-temperature SCR catalyst is focused on sulfur dioxide poisoning resistance.
Compared with high-temperature SCR, medium temperature SCR has the advantages of less waste heat power generation, less catalyst consumption, and lower flue gas resistance. Therefore, the author carried out this study.
1.2 Process layout
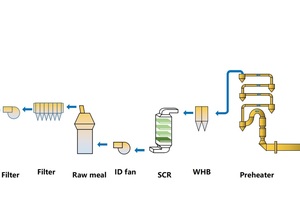
Medium temperature SCR reacts in the temperature window around 200-250 °C. Usually, the SCR reactor is arranged behind the waste heat boiler. Since the waste heat boiler can reduce the dust concentration by about 2-5%, the dust removal load of SCR is reduced, and the risk of dust blocking the SCR channel is also reduced. The flow chart of the medium temperature SCR system is shown in Figure 1.
The catalyst type is 13 hole honeycomb catalyst, which means that the cross section of each catalyst is 15 x 15 cm and each cross section has 13 x 13 holes. The catalyst tower has 4 layers in total. When the catalyst is installed in four layers, the total volume of the catalyst is 203 m3, and the gaseous hourly space velocity of the catalyst system is 1800 h-1.
Because the medium temperature SCR catalyst has higher vanadium content in order to cater to the low temperature, the SO2 conversion rate is higher than that of the common high temperature SCR. Ammonia, O2 and SO2 can react to form ammonium bisulfate. Ammonium bisulfate is solid at 200-250 °C, which is easy to block the SCR catalyst. Therefore, the SO2 content in the flue gas is required to be less than 50 mg/m3 in the current design. Nevertheless, the medium temperature SCR system still has the risk of resistance increase and denitration efficiency reduction caused by ammonium bisulfate, especially in the last SCR catalyst layer.
The medium temperature SCR denitration includes the ammonia delivery system, metering & injection system, SCR reaction tower, flue gas duct, catalyst, soot blowing system, compressed air system, ash conveying system, as well as corresponding electrical automation and instruments. After passing through the high-temperature fan, the flue gas from the kiln tail enters the SCR main reaction tower through the inlet flue expansion joint, inlet flue gas baffle door, ammonia spray gun and deflector. Then the flue gas after denitration treatment is discharged into the raw meal grinding system after passing through the expansion joint of the flue at the outlet of the tower and the flue gas baffle door at the outlet. The raw meal is dried and finally discharged after being collected by the exhaust fan. The dust entering the SCR main reaction tower with the flue gas from the kiln tail is about 100 g/m3. Part of the dust settles in the reaction tower and is discharged through the ash hopper and ash conveying system at the lower part of the reaction tower. Part of the dust is discharged from the reaction tower with the flue gas.
2 Experimental condition
2.1 Overview of production line
The SCR system is built in a 5000 t/d clinker line. The line has a double series 5-stage cyclone preheater, an online DD precalciner and a φ 4.8 x 72m rotary kiln. This line’s actual clinker consumption can reach 6400 t/h, and the standard coal consumption is 103 kg/t.cl.
The flue gas volume of the chimney is 700000 m3/h in working condition, and 500000 m3/h in standard condition. The initial NOx emission concentration is 500-600 mg/m3, and the actual NOx emission concentration is 60-100 mg/m3 by a set of SNCR system [5]. The ammonia concentration is 20%, and ammonia consumption is about 700 L/h which means ammonia consumption is 2.5 kg/h per ton of clinker.
2.2 Experimental instruments
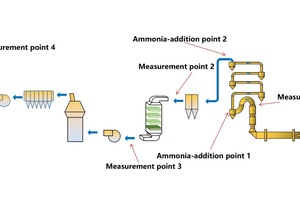
The optimal portable flue gas analyzer produced by the German MRU company is used to measure O2, NO and CO2 concentration. The ETG laser 6900 flue gas analyzer produced by the Italian ETG company is used to measure NH3 concentration. The location of measuring points and ammonia-addition points is shown in Figure 2.
3 Results and discussions
3.1 NOx and ammonia emission with medium
temperature SCR
The gas composition test results are as Table 1 under continuous and stable operation, with NOx ≤50 mg/m3 and NH₃ ≤5 mg/m3. SNCR and medium temperature SCR are both used in this production line, which can ensure that the emission concentration of nitrogen oxides and ammonia meets the most stringent standards.
3.2 Denitration efficiency of SCR
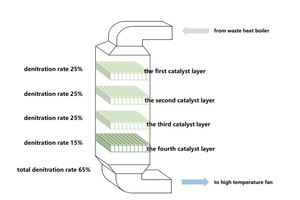
In the laboratory, the denitration efficiency of the same medium temperature SCR catalyst can reach more than 90% under GHSV 3000. However, in practical application, when the NSR is greater than 1, the denitration efficiency is about 55%-85%, and the average is 65%. Therefore a cement plant with only SCR without SNCR can not meet the NOx limit. The denox rate of each layer of catalyst is shown in Figure 3. The denitration efficiency of the first, second and third catalyst layers is similar and more than the fourth layer. After measurement, it is found that the gas resistance of the first/second/third catalyst layer is 50-80 pa, while the resistance of the fourth catalyst layer is as high as 150-200 pa. Therefore, it can be considered that the actual flue gas speed in the catalyst layer increases and the effective contact time decreases due to the blockage of the pores of the fourth catalyst layer. It can be seen that reducing the resistance of the catalyst layer is beneficial to improve the denitration effect of SCR.
3.3 Influence of ammonia dosage
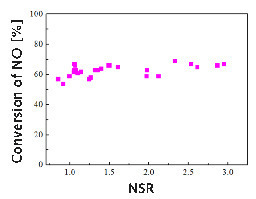
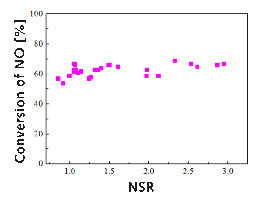
Can the denitration effect of medium temperature SCR be improved by increasing the amount of ammonia? The author uses NSR to express the ratio of ammonia/NO by injecting ammonia in ammonia-addition point 2. As shown in Figure 4, when NSR is from 0.8 to 2.9, the denitration rate only increases from 54% to 68%. It is meaningful to ensure NSR more than 1. However, it is not a cost-effective method to improve the denitration efficiency of medium temperature SCR by increasing the amount of ammonia.
3.4 Influence of ammonia addition position
There are two ammonia injection points in this project. Part of the ammonia spray guns are arranged at the outlet of the calciner and the outlet of the cyclone 5 which is the traditional SNCR location. The other guns are arranged at the outlet of the cyclone 1. Under the same total ammonia flow rate, we compared the injection of all ammonia at the traditional SNCR location with 50% at the traditional SNCR location and 50% at outlet of the cyclone 1. As shown in Figure 5, the traditional SNCR location is a good place for a hybrid SNCR/SCR system.
When all ammonia is injected at the traditional SNCR position, ammonia first reacts with NO under SNCR reaction conditions, and then reacts with NO in SCR again. In contrast, the ammonia added at the outlet of the outlet of cyclone 1 can only react with nitric oxide once in SCR. Therefore, it is a good choice to add all ammonia in the traditional SNCR position.
3.5 NO concentration
Under the condition that NSR at SCR inlet is guaranteed to be 1.0-1.2, the authors change the concentration of NOx at SCR inlet, and investigate whether the NOx concentration affects SCR denitration efficiency. The NOx concentration under five working conditions is 104, 152, 213, 267 and 302 mg/m3. The results are shown in Figure 6.
Different NOx concentrations have little impact on the denitration efficiency of each layer of catalyst, and the overall denitration efficiency is stable at about 65%.
3.6 Ammonia emission
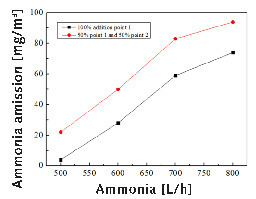
Ammonia emissions are now receiving increasing attention in China. At present, there is no clear Chinese official method to measure ammonia emissions from the cement industry. The authors measure the ammonia emission of medium temperature SCR system by the laser method and the results are shown in Figure 7. It can be seen that SCR cannot guarantee that the ammonia emission caters to the limit. The reasonable ammonia injection position and the low total amount of ammonia are both needed to meet environmental protection standards.
Fortunately, after many commissioning and experiments with all ammonia sprayed at injection point 1 and the ammonia flow under 500 L/h, this project can meet the stringent emission standards (NOx ≤ 50 mg/m3 and NH3 ≤ 5 mg/m3). This also shows that a cement plant must have the hybrid SCR and SNCR system to meet such a strict emission standard.
The low initial nitrogen oxide concentration and low total ammonia consumption in this production line are one of the reasons for meeting the requirements (NOx ≤ 50 mg/m3 and NH3 ≤ 5 mg/m3). Therefore, facing the production line with high initial NOx concentration, meeting the requirements is still a challenge.
4 Summary
We explored the situation of medium temperature SCR in the cement industry. The main research results are as follows:
We use SNCR and medium temperature SCR technology together and can cater to the stringent standards (NOx ≤ 50 mg/m3 and NH3 ≤ 5 mg/m3).
The denitration efficiency of the medium temperature SCR catalyst in industry is lower than that in the laboratory. Under the space velocity of the catalyst system 1800 h-1, the average denitration efficiency is only about 65%.
Ensuring NSR a little more than 1 is beneficial to improving the denitration efficiency, but it is not significant to continue to increase NSR.
Spraying ammonia at the traditional SNCR position is beneficial to the SCR system. While it is not necessary to set the SCR spray gun separately.
The denitration efficiency of SCR is stable under different nitrogen oxide concentrations.
Ammonia emission is still a possible problem for the medium temperature SCR system.

Überschrift Bezahlschranke (EN)
tab ZKG KOMBI EN
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
tab ZKG KOMBI Study test
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.