Application of pollution reduction technology in China’s cement industry
The cement industry is a major contributor to global carbon and NOx emissions, accounting for 7% of global carbon emissions and more than 10% of NOx emissions. As concerns about climate change and environmental pollution grow, the need to reduce carbon and NOx emissions in the cement industry becomes increasingly urgent.
This paper introduces the technical paths to reduce carbon and NOx emissions in the cement industry, and is supplemented by typical cases to illustrate the application effects achieved by cement enterprises in the above areas, and looks forward to the application prospects of pollution reduction and carbon synergy technologies in the cement industry.
1 Development of denitrification technology
1.1 Historical NOx emissions
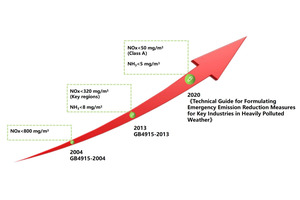
The total NOx emissions of China’s cement industry reached 2.3 million t in 2011. At that time emission from cement plants without any denitrification technology was 400-1200 mg/m3, with an average of 800 mg/m3. China’s “Emission Standard of Air Pollutants” issued in 2013, required NOx to be below 400 mg/m3. By 2017, total NOx emissions fell by more than half to 1 mt. Since 2019, many provinces have issued ultra-low emission standards of 50 or 100 mg/m3. China issued the “Technical Guide for the Formulation of Emergency...
1 Development of denitrification technology
1.1 Historical NOx emissions
The total NOx emissions of China’s cement industry reached 2.3 million t in 2011. At that time emission from cement plants without any denitrification technology was 400-1200 mg/m3, with an average of 800 mg/m3. China’s “Emission Standard of Air Pollutants” issued in 2013, required NOx to be below 400 mg/m3. By 2017, total NOx emissions fell by more than half to 1 mt. Since 2019, many provinces have issued ultra-low emission standards of 50 or 100 mg/m3. China issued the “Technical Guide for the Formulation of Emergency Emission Reduction Measures for Key Industries in Heavily Polluted Weather” in 2020, requiring the NOx emission limit for large enterprises of 50 mg/m3. More than 95% of Chinese cement plants are now equipped with Selective Non-Catalytic Reaction (SNCR), and 10% have Selective Catalytic Reaction (SCR) systems. NOx emissions of China’s cement industry are expected to drop to 0.5 mt in 2025.
1.2 Low NOx combustion technology
TCDRI calciner denitrification uses multi-stage air separation, multi-stage coal and material feed to reduce NOx generated by 60. The company developed new generation deep self-denitrification technology in 2022, which is characterized by improving denitrification efficiency and ensuring full burnout of fuel through significant increase in the height of the strong reduction zone and main combustion zone so as to reduce NOx generated by more than 70%.
This technology has been applied in more than 30 production lines. For example, in Tengzhou Dongguo Cement the NOx emission at the calciner outlet was less than 280 mg/Nm3. In order to achieve the ultra-low emission target of 50 mg/Nm3, ammonia consumption per unit of clinker was only 2.5 kg/t clinker, and the denitrification cost was significantly lower than that of similar production lines in the region. In addition, with the preheater outlet temperature below 240 °C, the specific heat consumption was less than 2.8 GJ/t clinker.
1.3 SNCR technology
TCDRI started research on SNCR in 1997 and established China’s first cement kiln denitrification system in Sinoma Xiangtan Cement in 2011. System improvements in 2019 strengthened the mixing of ammonia and flue gas by multi-point injection and other improvements to lower emissions and optimize use of ammonia. The minimum emission concentration of NOx can be controlled below 50 mg/m3 in some plants.
1.4 SCR technology
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology mixes ammonia or urea and other amino sub-stances with flue gas under certain conditions in the presence of a catalyst to reduce NOx to non-toxic nitrogen and water. The chemical equation is the same as SNCR:
4 NH3+ 4 NO+ O2 → 4 N2+ 6 H2O
4 NH3 + 2 NO2+ O2 → 3 N2+ 6 H2O
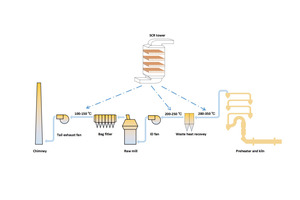
SCR technology can be divided into high-temperature SCR, medium temperature SCR and low-temperature SCR systems based on different locations of SCR catalysts in cement process, as shown in Figure 2.
High-temperature SCR can be divided into:
high-dust SCR,
low-dust SCR, and
integrated dust removal & denitrification, handling different dust concentrations
In the case of the most common technology of high-temperature high-dust SCR, the denitrification tower is at the outlet of the primary cyclone, with dust concentration of approximately 100 g/m3. It is extensively used due to the lowest investment in SCR systems. However, it is difficult to reach consistent results due to the deposition of dust and reduced service life of the SCR catalyst. Therefore, some researchers designed additional electrostatic precipitators and high-temperature bag filters in front of the SCR tower to reduce dust concentration. According to the experience of TCDRI, the electrostatic precipitator is not suitable due to large specific resistance of dust at the outlet of the primary cyclone. Consequently, this method has been rarely used. Installing a high-temperature bag filter in front of the SCR tower can reduce the dust concentration of a SCR tower to approximately 10 mg/m3, so that the SCR catalyst works in a dust-free state. This is very beneficial to the activity and life of the catalyst, but it requires high total investment. TCDRI is studying the denitrification mode of integrating a high-temperature bag filter and SCR catalyst at present.
As more cement lines upgrade from stage-five to stage-six pre-heaters, and the outlet temperature of the primary cyclone is reduced below 280 °C, power generation of the waste heat recovery systems declines. In order to maintain the power generation capacity as much as possible, the SCR catalyst tower is arranged after the waste heat power generator using a medium-temperature SCR system. TCDRI has installed more than 10 such systems. They have stable denitrification efficiency close to high-temperature SCR.
High-temperature SCR is the most widely used with 100 installations in China, medium-temperature SCR is used by more than 20 lines, and the low-temperature SCR system is still in the research and development stage and has yet to be industrialized.
1.5 SCR case study
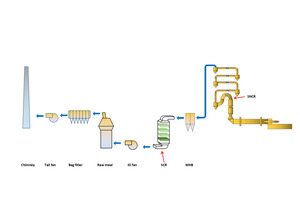
South Cement (Baixian) in Huzhou, Zhejiang has a 5000 t/d cement clinker production line by using a stage-five pre-heater. A medium-temperature SCR system developed by Tianjin Cement Industry Design & Research Institute was installed as shown in Figure 3.
Before the project, the initial NOx emission concentration was 500 mg/m3. With the SNCR system using 2.0 kg/t.cl ammonia, and no additional ammonia in the SCR system, the NOx concentration at the outlet of the stage-one cyclone was 100 mg/m3 and the NOx emission concentration from the stack was less than 35 mg/m3. Ammonia escape concentration was less than 5 mg/m3.
2 Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS)
CCS projects have the potential to not only reduce CO2 emissions but also other pollutants such as NOx and SO2 that are found in the flue gas.
There are 5 carbon capture methods recognized as practical for cement:
MEA chemical absorption
oxy-fuel combustion
chilled ammonia
membrane separation
tail-end and integrated calcium looping
Oxy-fuel combustion uses high-concentration O2 for clinker sintering, generating relatively high-purity CO2 which can be stored after purification and compression. It has cost advantages compared with other methods.
2.1 Development of TCDRI’s oxy-fuel technology
During its research work, TCDRI identified oxy-fuel combustion technology as the key research and development direction for carbon emission reduction in February 2019, and completed a research platform for oxy-fuel combustion in association with Cement AG and the Huazhong University of Science and Technology. TCDRI has developed technical proposals for oxy-fuel combustion and low-energy carbon capture technology for South Cement and CUCC. TCDRI had applied for 31 patents related to oxy-fuel combustion carbon emission reduction technology by the end of 2022.
TCDRI’s system is composed of:
CO2 self-enrichment system
oxygen generation system
flue gas capture and purification system
The oxygen generation system is used to provide high-purity oxygen for the CO2 self-enrichment system that increases CO2 concentration in flue gas to more than 80%. The flue gas capture and purification system produces industrial and food-grade liquid CO2 through a combination of flue gas pretreatment + pressure swing adsorption concentration + variable-temperature and pressure swing adsorption purification + liquefaction distillation.
Oxy-fuel combustion coupled with low-energy carbon capture technology independently designed and developed by TCDRI consumes 1.6-1.7 GJ/t.CO2, energy consumption and operating costs are 25% less than that of conventional chemical absorption methods.
TCDRI established an oxy-fuel test platform in August 2022. The project team has completed the following experimental research:
selection of atmosphere for industrial application of oxy-fuel combustion by monitoring the combustion flame under different O2 concentrations;
examination of different O2/CO2 combustion atmospheres through circulating flue gas + industrial oxygen to obtain dry basis CO2 concentration of 80-85% from the calciner, which is more than three times higher than conventional air combustion;
optimizing the decomposition rate of raw materials to reach > 90% by controlling the temperature distribution in the calciner
In order to reach industrial and food-grade liquid CO2, the VPSA vacuum method is used to concentrate CO2 gas to approximately 95%, then desulfurization and denitrification technology removes traces of organic sulfur and NOx, after which the PTSA adsorption process and the low-temperature liquefaction distillation purification process are then used.
3 Prospects for reducing environmental impact
The reduction of NOx emissions in China provides an example of how the cement industry can rapidly improve its environmental performance once the technology roadmap to do so is clear and with strict enforcement of increasingly challenging emission limits. This provides a blueprint for CO2 reduction. Developments in CCS technology such as oxy-fuel offer a pathway to achieve carbon neutrality.
To make carbon neutrality a reality, requires:
a unified and standardized carbon emission calculation system for the cement industry, including scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions, making the most of digital technologies to measure and track emissions
incentives to accelerate research and development as well as application of CCS technologies, policies to close old, inefficient production capacity
Cement enterprises should actively communicate and cooperate with governments to jointly promote the sustainable development of the cement industry and achieve a virtuous cycle of economic benefits and environmental protection.

Überschrift Bezahlschranke (EN)
tab ZKG KOMBI EN
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
tab ZKG KOMBI Study test
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.