Application of a high-temperature & low-dust SCR in a cement plant
With the improvement of environmental protection standards, more and more denitration technologies are applied in Chinese cement plants. Even SCR technology alone has different processes such as high-temperature & high- dust SCR, high-temperature & low-dust SCR, medium-temperature & high-dust SCR, low-temperature & low-dust SCR. Taking the high-temperature & low-dust SCR system in a 5000 t/d cement clinker line as an example, the author introduces the technical process and operation situation.
The ultra-low emission of nitrogen oxides is a major problem faced by Chinese cement plants in recent years. Almost all Chinese provinces require the emission concentration of nitrogen oxides to be lower than 100 mg/m3, and even some provinces require the NOx emission to be lower than 50 mg/m3. Today there are several categories of denitration technologies that have been applied in the Chinese cement industry, such as low-NOx combustion [1], SNCR [2], SCR [3], and LCR (integration of wet desulfurization and denitration) [4]. Among them, the SCR technology has been also widely used in the...
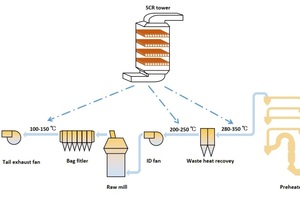
The ultra-low emission of nitrogen oxides is a major problem faced by Chinese cement plants in recent years. Almost all Chinese provinces require the emission concentration of nitrogen oxides to be lower than 100 mg/m3, and even some provinces require the NOx emission to be lower than 50 mg/m3. Today there are several categories of denitration technologies that have been applied in the Chinese cement industry, such as low-NOx combustion [1], SNCR [2], SCR [3], and LCR (integration of wet desulfurization and denitration) [4]. Among them, the SCR technology has been also widely used in the thermal power generation industry. Combining with the cement process, a variety of SCR technologies with cement industry characteristics have been derived as Figure 1.
The high-temperature SCR tower is arranged between the highest cyclone and the waste heat power generation, and the working temperature ranges from 280 to 350 °C. Depending on whether there is a dust filter in front of the SCR tower, the high-temperature SCR can be divided into high-tempera-ture & high-dust SCR and high-temperature & low-dust SCR. The medium temperature SCR tower is arranged between the waste heat power generation and the high temperature fan, and the working temperature ranges from 200 to 250 °C. The low temperature SCR tower is arranged between the bag filter and the tail exhaust fan, and the working temperature ranges from 100 to 150 °C.
Among these three processes, the high-temperature SCR process is widely used in China‘s cement industry [5, 6] because it is close to the working temperature of the SCR catalyst in ordinary power plants. Due to the high concentration, viscosity and alkali metal content of dust, the working environment of the catalyst is relatively harsh, so the dusty SCR system is easily blocked and worn. Under the same conditions, the denitration efficiency and service life are lower than those SCR of power plants. Therefore, some companies add a dust collector (electric dust collector alone, bag filter alone, electric + bag filter) in front of the high-temperature SCR tower to solve the problems of blockage and wear caused by dust in process. As the particle characteristics from the highest cyclone are not suitable for being captured by the electrostatic dust collector, only a high-temperature SCR with a bag filter can be called a high-temperature & low-dust SCR.
1 Project overview
The cement plant located in South China has a 5000 t/d clinker production line. In 2020, the Chinese government issued a technical guide for formulating emergency emission reduction measures for key industries with heavy pollution weather, which announced that the NOx emission should be lower than 50 mg/m3, and the ammonia emission should be lower than 5 mg/m3 for class A cement enterprises. Furthermore, class A enterprises can get more running days in a year. The China Cement Association has issued the ultra-low emission standard of air pollutants for the cement industry (group standard), which limit NOx to under 100 mg/m3, and ammonia emission to under 8 mg/m3.
In order to reduce the environmental emission risk, to get more running days and fulfill social environmental responsibility, this plant decided to add an SCR system and chose the high temperature & low-dust SCR.
2 Before adjustment
In 2013, the plant installed an SNCR system designed by the author, which can control NOx emission concentration to below 100 mg/m3. The SNCR system injects ammonia water at the outlet of the calciner and the lowest cyclone.
The plant has a conventional five-stage preheater system. The flue gas from the preheater passes the WHR, then goes through the ID fan and the raw mill. After the bag filter, the flue gas enters the atmosphere through the tail exhaust fan and the chimney.
The problems of this project before adjustment are as follows: First, NOx emission concentration cannot be controlled below 50 mg/m3, which does not meet the standard of Class A. Second, when the NOx emission is controlled below 100 mg/m3, the amount of ammonia water is high at present. The consumption of 20% ammonia water per ton of clinker is 3-5 kg/t.cl, so the running cost is expensive. Third, the ammonia emission concentration is higher than 5 mg/m3, which does not meet the Class A standard either.
3 The high-temperature & low-dust SCR process
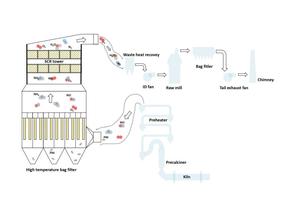
The process is shown schematically in Figure 2. A high-temperature bag filter is added at the outlet of the highest level cyclone, and then a high-temperature SCR tower follows the filter. The dust concentration in the flue gas decreases from nearly 100 g/m3 to 10 mg/m3 after passing through the high-temperature bag filter. The catalyst is always in the clean atmosphere, and its activity and service life are effectively guaranteed. The flue gas status is shown in Table 1. The design parameters are shown in Table 2.
4 Results and discussions
4.1 The state of operating system
After the project is put into operation, all technical indicators have reached the design standards. Although the initial NOx concentration of this clinker line is high and the SNCR system is not running, the ammonia water consumption is acceptable. This system’s total pressure loss is about 1000-1200 Pa, which is more than that of the high-temperature & high-dust SCR with the pressure loss of 500-700 Pa.
4.2 NOx and ammonia emission
Up to now, the system has been running continuously for nearly a year. Without SNCR, the NOx emission concentration keeps below 50 mg/m3, and NH3 emission concentration is lower than 5 mg/m3. In fact the high-temperature & low-dust SCR can ensure that the NOx emission concentration is stable below 20 mg/m3. Denitration efficiency is always higher than 90%. These results reflect its strong denitration capability.
4.3 Denitration efficiency of SCR
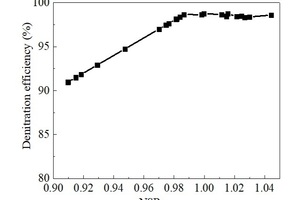
In the laboratory, the denitration efficiency of SCR can easily reach over 95% under GHSV 3600 h-1. However due to dust blockage, abrasion and other reasons in the flue gas, the denitration efficiency in the factory generally cannot reach the laboratory level. Especially in the cement industry, the denitration efficiency of a high-temperature & high-dust SCR is mostly 90%. Fortunately, after the high-temperature bag filter, the SCR’s denitration efficiency of this project can easily reach over 95%. The author uses NSR to express the ratio of ammonia/nitric oxide. It can be seen from Figure 3 that with the increase of NSR, the denitration efficiency increases synchronously. However, when the NSR reaches 0.98, further increase of NSR will not improve the denitration efficiency. Therefore, from the perspective of controlling operating costs, it is appropriate to control NSR at around 0.95.
4.4 Ammonia emission
The ammonia emission concentration of this project is from the online monitoring data. When the raw mill is running, the ammonia emission concentration meets the emission standard steady. The data in Figure 4 are recorded when the raw mill is shut down. When NSR is lower than 1, the ammonia emission concentration is always very low, which is approximately negligible. However, when NSR is more than 1, the surplus ammonia cannot participate in the reaction and is forced to be discharged from the chimney. Therefore, it is necessary to control NSR below 1 to ensure that the emission concentration of ammonia reaches the standard.
4.5 Advantages
The high-temperature & low-dust SCR system has the following advantages comparing with the high-temperature & high-dust SCR system.
Long-term stable operation:
The SCR catalyst is in a nearly dust-free environment and hard to be blocked, worn or poisoned by high concentration of dust. Therefore, the catalyst is always in a highly active state, so NOx emission and ammonia emission are stable. In addition, the workload of workers to remove the catalyst blockage almost disappeared.
Low catalyst consumption:
After the high concentration dust is collected in this project, there is no problem of dust blockage. Therefore, the catalyst with a high number of holes (25 holes) can be selected. Its surface area is twice that of the traditional catalyst with a low number of holes (13 holes). The catalyst volume is only 1/2 of the amount of high-temperature & high-dust SCR catalyst. Only two layers of catalyst need to be arranged. In China, the waste SCR catalyst is treated as the hazardous waste, so the waste SCR catalyst generated by this technology is also little.
Low oxidation rate of sulfur dioxide:
The SCR tower is only equipped with two layers of catalyst. Compared with high-temperature & high-dust SCR technologies with 4 or 5 layers of catalyst, its GHSV is double. So the oxidation rate of sulfur dioxide is lower, which will weaken the corrosion of ammonium bisulfate and other substances on subsequent cement process equipment.
Low NOx emission concentration:
Compared with the high-temperature & high-dust SCR which has a 90% denitration efficiency, the denitration efficiency of this process can be stable at about 95%, so the ultra-low NOx emission can be guaranteed. At the same time, there is no need to worry about the problem of excessive ammonia emission concentration. In addition, the SNCR system is no longer necessary.
Low running cost:
For power consumption, more of the ID fan’s electric energy is needed due to more flow gas resistance. Fortunately the high-temperature & low-dust SCR honeycomb needs to be less purged, which is the high-temperature & high-dust SCR’s main power consumption. According to our statistics, the total power consumption of the high-temperature & low-dust SCR is slightly higher than that of a high-temperature & high-dust SCR because of the filter’s pressure loss. Fortunately, the high-temperature & low-dust SCR has a slight advantage over the high-temperature & high-dust SCR in the catalyst life, the hazardous waste disposal cost and the maintenance cost. Overall, the operating cost of the high-temperature & low-dust SCR is slightly lower.
4.6 Disadvantages
The high-temperature & low-dust SCR’s main disadvantage is the high investment cost because of the high temperature bag filter. For a 5000 t/d clinker line, an additional high-temperature bag filter will increase the investment by about two million euros, which is on the premise that buildings and structures are not considered. For old production lines, due to the shortage of space, most of the newly added high temperature bag filter needs to be erected separately, so the construction and structure costs should not be underestimated. The high-temperature & low-dust SCR system is one and a half million euros more expensive than the high-temperature & high-dust SCR in the Chinese market.
As an additional high-temperature bag filter is added, the pressure loss increases. Without considering the pipeline, the high-temperature & low-dust SCR tower’s pressure loss is 120-150 Pa and the additional high-temperature bag filter is 600-700 Pa. However the high-temperature & high-dust SCR tower’s pressure loss is 300-400 Pa without the pipeline. So the power consumption of the tail exhaust fan of the plant with a high-temperature & low-dust SCR needs to be increased.
In addition, the high-temperature & low-dust SCR will reduce the temperature of flue gas entering the WHR. In actual operation, the gas temperature at the WHR inlet is 10-12 °C lower than that without the high-temperature & low-dust SCR. This is a negative impact on the waste heat recovery.
5 Summary
As above, the high-temperature & low-dust SCR system has many advantages such as long-term stable operation, low catalyst consumption, low oxidation rate of sulfur dioxide, low NOx emission concentration and low running cost. But because of the addition of a high temperature bag filter, its investment is higher than the high-temperature & high-dust SCR. The author believes that this technology is more suitable for areas with higher environmental requirements.

Überschrift Bezahlschranke (EN)
tab ZKG KOMBI EN
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
tab ZKG KOMBI Study test
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.