Cause analysis and solutions for ESP corrosion
Kiln back-end electrostatic precipitator (ESP) of an Egypt cement plant experienced severe corrosion within one year of operation. Based on the chemical composition of samples, calculation of the acid dew point and XRD analysis of rust powder, ESP corrosion reasons were found, including the high chloride content in raw meal, high water vapor content, the severe air leaking. Solutions were proposed.
1 Introduction
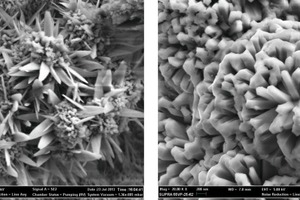
Severe corrosion occurred on the pole wire, pole plate, shell (Fig. 1) of the kiln back-end electrostatic precipitator (ESP) within one year after...
1 Introduction
Severe corrosion occurred on the pole wire, pole plate, shell (Fig. 1) of the kiln back-end electrostatic precipitator (ESP) within one year after commissioning. The ESP dust collection efficiency reduced significantly, which affected the normal operation. During the kiln shutdown, internal surfaces of ducts from ID fan to ESP fan, conditioning tower, ESP, bucket elevator and air slide seemed wet and muddy due to water absorption by material particles. Liquid gathered from the ESP had a PH value of 6.
2 Iron rust and ESP corrosion
Generally, the reasons for ESP corrosion include caustic gas, high moisture content, high air leakage rate, uneven gas velocity, ineffective heat preservation for the shell and so on. However, which factor is the culprit for the ESP collapse of this plant within extremely short time?
3 Cause analysis
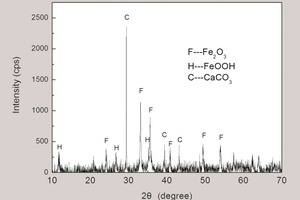
Studies show that pyrite and organic sulfur in raw materials are oxidized to form SO2 at temperatures between 400 °C and 600 °C, preferably in cyclone Stage II or Stage III. Also, combustible chlorine appears in gas mostly in the form of HCl in the temperature range 300 °C ~ 600 °C. To evaluate the gas composition, raw meal was calcined at 600 °C. The results and assumed conditions are displayed in Table 2.
After the above-mentioned low-temperature calcination, the SO3 content of raw meal decreased from 0.35 % to 0.31 % and the Cl content decreased from 0.207 % to 0.148 % (the mass loss had been considered). The previous studies [1] show that the cyclones at the lower temperature end are much less efficient in removing SO2 with CaCO3, due to the combined effects of low temperature and the small amount of CaO or Ca(OH)2. Thus ignoring the SO2 and HCl removal from the upper preheater stages, SO2 and HCl concentration from C1 flue gas was 340 mg/Nm3 (119 ppm) and 645 mg/Nm3 (396 ppm), respectively.
During the operation, the flue gas from C1 maintained a low temperature of 280 °C. When the raw mill was off, the ESP inlet gas temperature was approximately 140 °C and the outlet gas temperature was only 85 °C. When the raw mill was on, the ESP inlet gas temperature was merely 100 °C to 120 °C.The water dew point and the acid dew point of hydrochloric acid of the flue gas are far below the flue gas temperature from ID fan to ESP fan. The liquid condensation on the equipment wall is ascribed to the presence of gaseous sulfuric acid, the acid dew point of which is much higher.
It is induced that the present gaseous HCl in the ESP inlet gas leads to the high Cl content of 1.698 % for the rust powder scraped from ESP plate. Meanwhile, ash from ESP contains a high Cl content, as shown in Table 1.
To sum up, the high chloride content of 0.207 % in raw meal is responsible for the ESP corrosion in this plant. The reaction occurring on the ESP plate is the oxygen-consuming corrosion, while more importantly, chlorine favor the corrosion and cause the collapse within such a short time. Of course, the high water vapor content due to the combined effects of firing natural gas and the local moist climate is a necessity for the accelerated corrosion. It is worth mentioning that the large temperature difference of 55 °C between the ESP inlet and outlet gas indicates the severe air leaking, which is the main inducement for the corrosion.
4 Solutions
Take all measures to guarantee the ESP seal and reduce the air leaking rate.
Enhance the heat preservation performance of the ESP shell.
Past experiences show that keeping the flue gas temperature 30 °C above the acid dew temperature is effective in retarding the corrosion. For this plant, the ESP inlet gas temperature should reach 150 °C or higher. It can be realized by adjusting the feeding point in the preheater tower.

Überschrift Bezahlschranke (EN)
tab ZKG KOMBI EN
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
tab ZKG KOMBI Study test
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.