Technology development and industrial application of large-scale TRM vertical roller mill
This paper addresses several new challenges associated with the large-scale operation of TRM vertical roller mills, including equipment stability, structural reliability, and process system optimization. The grinding team at Tianjin Cement Industry Design & Research Institute Co., Ltd. has conducted innovative research in these critical areas, resulting in significant breakthroughs. The successful research and development, design, and industrial application of large-scale cement and slag vertical roller mills have led to marked improvements in the technical performance of grinding equipment. These research findings establish a solid foundation for the sustainable development of grinding technology and equipment and provide valuable insights for advancing technology in the cement industry.
1 Background
With continuous technological advancements in the cement industry, the production scale of new dry cement clinker is expanding, leading to a trend towards larger equipment. Economically, large-scale grinding equipment offers significant advantages for intensive production, effectively reducing both investment and operating costs. Additionally, the large-scale equipment also promotes process flow optimization, minimizes losses in intermediate links, and significantly improves production efficiency. Moreover, large-scale equipment contributes to lower energy consumption and...
1 Background
With continuous technological advancements in the cement industry, the production scale of new dry cement clinker is expanding, leading to a trend towards larger equipment. Economically, large-scale grinding equipment offers significant advantages for intensive production, effectively reducing both investment and operating costs. Additionally, the large-scale equipment also promotes process flow optimization, minimizes losses in intermediate links, and significantly improves production efficiency. Moreover, large-scale equipment contributes to lower energy consumption and emissions, promoting sustainable development. Overall, the adoption of large-scale equipment in the cement industry not only reflects technological progress but also represents a strategic choice for enhancing economic efficiency and remaining competitive in the market.
The Tianjin Cement Industry Design & Research Institute Co., Ltd. (TCDRI for short) has been committed to the research and design of grinding equipment in the field of cement since the1980s. Over the years, the institute has built a substantial technical foundation and assembled a professional talent team for the research, development, design, and manufacturing of grinding equipment. Currently, TCDRI’s products has been applied to more than 1000 sets across various fields, including cement raw materials, metallurgical slag, and cement clinker [1]. Notably, TCDRI has been recognized as a single champion demonstration enterprise in the manufacturing industry for its vertical roller mill.
In the process of large-scale vertical roller mills, a series of new problems such as equipment stability, structural reliability, process system optimization and intelligence are to be faced. This paper focuses on the innovative technology research and development of TCDRI in this field and the in-depth research work to address these challenges [2-3].
2 Key technology development
2.1 Material flow rate control technology
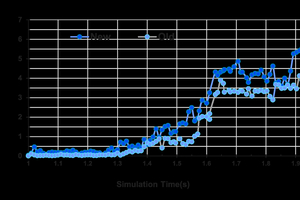
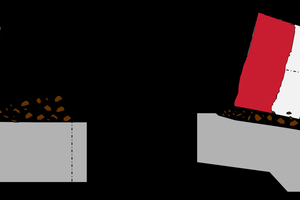
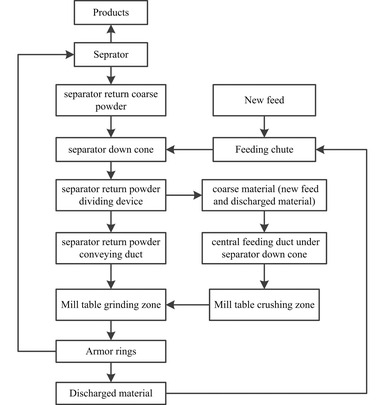
By simplifying the simulating model of vertical roller mills (VRM) to exclude the influence of the grinding roller on the movement of material particles, we focus solely on the feeding port and the grinding table, which moves in uniform circular motion around its own axis. Using EDEM software, we constructed the grinding structure model of the VRM and imported the relevant settings to create a simulation model reflecting the operating conditions of the vertical roller mill. Aiming at the problems of poor bed-grinding stability and low operating power of the large-scale cement vertical roller mill, the above simulation method has been used to research and design grinding structure of VRM, and the material flow control technology was developed to make roller and table form the best fit structure and effectively control material flow state on table. which solves the problem of fast flow rate and poor controllability of flow state, at the same time, this technology can prolong the residence time of materials on table and broaden the length of grinding area, which achieves the effect of improving grinding efficiency and reducing grinding energy consumption.
By comparing the simulation results of old and new grinding structure forms (refering to Figure 1 and Table 1), we found that adjusting the bite angle between the table and the roller can effectively increase the feed rate by 37.8%. This adjustment also corresponds to a significant increase in the absorbed power of the main motor by approximately 23.7%. Notably, grinding efficiency improved by 23.7%, while the power consumption of the main motor decreased by 10.3%.
Figure 2 shows the comparison of wear conditions in the grinding area between old and new grinding structure forms. The high-pressure grinding area for old grinding structure is mainly concentrated at the larger end of grinding roller. After applying this technology, the grinding area can be expanded to cover half, or even the entire surface of the grinding roller, which can reduce the local force and minimizes the risk of surfacing layer spalling due to stress concentration at the large end of grinding roller.
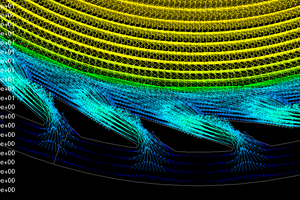
2.2 Static separation technology
Given the challenges associated with traditional cage separators, such as low separation efficiency and high linear speeds, especially in large-scale vertical roller mills with increasing separator diameters, it is evident that the structural form and design parameters of a static blade can no longer adhere to conventional design. Therefore, it is necessary to re-develop new structural shape and design parameters. In this context, the grinding team developed a new triangular static blade, with EDEM simulation results shown in Figure 3. It can be seen that the windward side of static blade effectively reduces the pulling force on coarse particles in the gas, thereby increasing the passage time through the blade and facilitating preliminary sorting of coarse particles. This improvement in primary separation enhances the uniformity of particle sizes in the gas entering the gap between the dynamic and static blades, which indirectly improves the secondary separation clarity of dynamic blade. Additionally, the second baffle of the triangular static blade provides a secondary dispersion impact on finer particles in the gas, enabling effective secondary separation. The gradient spacing between each pair of static blades is designed to minimize resistance loss and facilitate the localized settling of coarse particles within the gas.
After extensive laboratory studies, the results indicate that separation efficiency has increased by 10 to 20%. Additionally, the content of fine particles below 30 μm has risen, resulting in a broader particle grading in the product. The n value has reached below 0.8, and the particle size distribution is now more extensive, which helps to reduce the water requirement for normal consistency.
The separation efficiencies of various static blade shapes were measured, and the results are presented in Table 2. The triangular static blade achieves a separation efficiency of 75% to 78%, which is 10% to 15% higher than that of the traditional static blade. Furthermore, the triangular static blade helps reduce the resistance in the cement vertical roller mill, lowering it to 4000 to 4500 Pa, representing a reduction of approximately 30%.
2.3 Stress analysis of key grinding structures
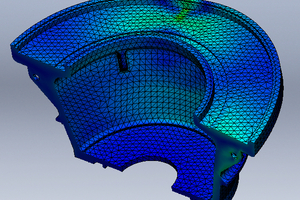
For the strength design of key grinding components in large-scale vertical roller mills, we utilize advanced software to perform stress analysis on each essential component and grinding structure. This analysis guides the development and design of the vertical roller mill based on the findings from a computer analysis. The primary focus includes the stress analysis of the grinding table and both the upper and lower rocker arms.
Building on the previous development of the TRM vertical roller mill series, we initially simplified the model to prevent issues related to stress concentration and mesh division caused by intricate structural geometric details. Consequently, features such as small holes, chamfers, and fillets were omitted. The load and constraint conditions were applied in accordance with the operating requirements of vertical roller mill. For the grid unit, we utilized a 4-node tetrahedral solid grid type, ensuring high-quality settings. Figure 4 below illustrates the stress analysis modeling of the grinding table. The analysis results indicate that stress on the grinding table is primarily concentrated in three areas, which are common failure zones and critical points for strength evaluation. Additionally, stress concentration is observed in the upper rocker arm, particularly around the air hole and the elbow, identified as weak links. The lower rocker arm also exhibits stress concentrations at two locations: one near the hydraulic pressure hole and the other at the junction where the shape of the rocker arm transitions.
Based on comprehensive stress and modal analysis research, we have optimized the structural dimensions of key components in the vertical roller mill after extensive simulations and comparisons. This ensures that the critical components of the slag and cement vertical roller mill exhibit high reliability in the large-scale process.
2.4 Grinding process system optimization
To address the issue of high heat consumption in large-scale slag vertical roller mills, we have researched and developed a “low resistance and low heat consumption technology”, as illustrated in Figure 5. This approach involves utilizing circulating residual heat air for the Hot Gas Generator (HGG) instead of fresh cold air, thereby maximizing the utilization of residual heat. By implementing this method, the resistance of the hot air entering the mill is minimized, allowing the circulating residual hot air to thoroughly mix with the high-temperature air from the HGG, which enhances the internal heat transfer efficiency of the vertical roller mill (VRM). As shown in Figure 6, our system process simulation demonstrates that the arrangement of the circulating air pipes, as well as the positioning and outlet pipes of the HGG, has been optimized. This not only reduces system resistance and improves the heat utilization rate of the HGG but also addresses the high heat consumption associated with traditional VRM grinding systems. Ultimately, this results in reduced energy consumption and lower production costs.
Using the TRMKS6031 cement and slag vertical roller mill as a case study, Table 3 below compares the system configurations before and after the implementation of traditional and new technologies. The findings indicate that, while maintaining the same grinding and drying capacity, the system flow rate has decreased by approximately 6%. Additionally, the fan power requirements have been reduced by 28%, heating capacity has decreased by around 20%, and the theoretical heat consumption has been lowered by 15% to 20% (refer to Table 4 for detailed information).
2.5 Remote diagnostic service system development
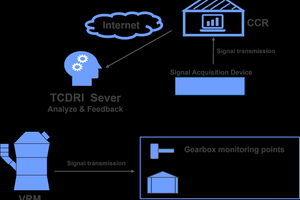
As science and technology continue to advance, intelligent production and manufacturing have increasingly become central goals for enterprises seeking to enhance their competitiveness. Leveraging big data analysis, TCDRI has developed a remote diagnosis service system (illustrated in Figures 7 and 8) designed to enable online monitoring and early warning of key equipment, thereby promoting the informatization of operational management. This system not only helps enterprises manage production costs across multiple factors but also facilitates remote customer service, leading to improved operating quality and stability of equipment.
The remote monitoring and diagnosis service system offers high-precision, real-time data monitoring for each production link, key equipment, process parameters, and product quality. Its specific functions include:
1) Real-time environmental data collection: The system continuously monitors the environmental parameters of the production site, capturing changes promptly to ensure that equipment operates under optimal conditions.
2) Real-time equipment diagnosis: By continuously monitoring the operating status of equipment, the system can promptly identify potential safety hazards, ensuring a safe production process.
3) Real-time and historical data analysis: The system enables in-depth analysis of both real-time and historical data to identify root causes and facilitate continuous improvement, thereby advancing the implementation of lean production.
4) Real-time early warning mechanism: By establishing key indicators and warning thresholds, the system can issue alerts at the initial stages of potential issues, allowing the operations team to intervene promptly and prevent minor problems from escalating into major failures, thereby ensuring timely pre-emptive control.
Through the systematic solution outlined above, companies can enhance production efficiency and product quality while optimizing resource utilization, contributing to the achievement of sustainable development goals. This intelligent transformation process will establish a stronger foundation for the future competitiveness of enterprises.
2.6 Large-scale TRM cement & slag vertical
roller mill series
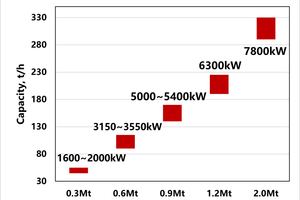
After over 20 years of continuous development and technological advancements, the TRM slag and cement vertical roller mill has successfully reached large-scale production. This significant milestone not only drives technological innovation in the cement industry but also offers the market more efficient grinding solutions. The TRM cement vertical roller mill is highly adaptable and efficient, with a single VRM capable of servicing clinker firing systems ranging from 1000 to 10000 t/d. Additionally, its grinding capacity for a single VRM accommodates production demands of 300000 t to 2 million t of GGBS annually, effectively meeting the operational needs of enterprises (see Figure 9 below).
In terms of energy efficiency, the system power consumption for grinding PO42.5 cement with TRM cement vertical mill has been significantly reduced to 20-22 kWh/t, while the system power consumption of grinding GGBS is maintained within 32 kWh/t. These outstanding energy efficiency metrics demonstrate the equipment‘s ability to reduce costs, providing substantial economic and environmental benefits to users. Given these attributes, the TRM slag and cement vertical roller mill holds a clear competitive advantage in the industry.
The breakthrough and implementation of these technologies not only enhance production efficiency and reduce energy consumption but also improve product quality, giving enterprises a competitive edge in a challenging market. Additionally, this advancement signifies a shift in large-scale grinding equipment towards greater efficiency, higher yields, and environmental sustainability, providing robust support for the development of the entire cement industry.
3 Industrial applications
As of June 2024, over 20 large-scale TRM slag and cement vertical roller mills with table diameters exceeding 6 m have been successfully sold on the market. This includes two cement vertical roller mills with a diameter of 6.3 m and two slag and cement vertical roller mills with a diameter of 6.6 m. Table 5 provides a partial sales list. All the vertical roller mills have been successfully installed and, after a brief commissioning period, have passed assessments and achieved the expected design capacity. This reflects their efficient production capabilities and stable operational performance. Owners have expressed high praise, noting that the mills not only enhance production efficiency but also optimize resource utilization and significantly reduce production costs.
Guangxi Yuansheng Slag Comprehensive Utilization Co., Ltd. is located in Fangchenggang City, Guangxi Province/China. Since 2012, the company has successfully implemented three large-scale slag and cement vertical roller mills with table diameters over 6 m from Sinoma (Tianjin) Powder Technology and Equipment Co., Ltd. The second line, established in 2014, and the third line, established in 2018, consist of TRM60.3 slag vertical roller mills, while Line 5 features the TRMKS66.4 cement and slag vertical roller mill.
Sihui Jun Ma Co., Ltd. is located in the Nanjiang Industrial Park in Sihui City, Zhaoqing/China. In 2020, the company signed a contract for the TRMS6031 slag mill with TCDRI. The heat source for drying is primarily supplied by the cooler from the clinker kiln within the plant. The vertical roller mill has an output of 210 to 225 t/h with a Blaine fineness of 420 m²/kg, and the system power consumption is less than 35 kWh/t. This marks a significant energy saving compared to the traditional slag vertical roller mill system, which consumes around 40 kWh/t.
4 Conclusion
By incorporating a variety of innovative technologies, the TRM slag cement vertical roller mill has demonstrated considerable advantages in technology, economy, and environmental protection. Compared to traditional structures, the design and development of large-scale slag and cement vertical roller mills have lowered system power consumption by 4 kWh/t, reduced drying heat consumption to less than 10 kg ce/t, and decreased overall energy consumption by approximately 2-3 kg ce/t - a reduction of up to 20%. These enhancements not only boost production efficiency but also minimize energy consumption.
Since the establishment of the project, TCDRI has sold over 20 sets of slag and cement vertical roller mills with a diameter of 6.0 m or more, with the TRMKS6031 model standing out as a flagship product. Its exceptional performance and technical advantages have led to impressive market success and competitiveness, earning the trust and praise of numerous customers.
To further reduce system power consumption and enhance the processing capacity of single equipment, TCDRI is advancing the development of larger-scale vertical roller mill technology based on existing innovations. At present, the development of a 7.0 m cement & slag vertical roller mill has been successfully completed. The introduction of this new equipment will further solidify the company’s market position and offer customers more advanced production solutions to promote industry growth.

Überschrift Bezahlschranke (EN)
tab ZKG KOMBI EN
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
tab ZKG KOMBI Study test
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.
This is a trial offer for programming testing only. It does not entitle you to a valid subscription and is intended purely for testing purposes. Please do not follow this process.